
ORGANIC ACIDS

Organic acids play a crucial role in enhancing the bioavailability and absorption of minerals present in organic food products. These naturally occurring compounds interact with minerals in a manner that significantly boosts their nutritional value, facilitating the body’s ability to absorb essential nutrients effectively. This function is particularly vital in the context of organic foods, which prioritize natural methods for enhancing and preserving nutrient content without the use of synthetic additives or chemicals. The importance of organic acids in nutrition cannot be overstated, as they contribute to the overall health benefits of organic foods. By improving mineral bioavailability, organic acids help ensure that the body can utilize the minerals present in these foods more efficiently. This is especially relevant for individuals who may have dietary restrictions or specific health concerns that affect nutrient absorption.
This is particularly advantageous for people who may be at risk of deficiencies, such as those with dietary restrictions or increased nutritional needs. By choosing organic options that naturally contain these acids, consumers can take advantage of their enhanced nutritional properties, ultimately supporting better health outcomes and promoting a balanced diet. Among the various organic acids, citric acid, malic acid, and lactic acid stand out due to their unique roles in enhancing mineral absorption .Citric Acid Found abundantly in citrus fruits, citric acid is known for its ability to chelate minerals, meaning it can bind to them and form soluble complexes. This process increases the solubility of minerals such as calcium, magnesium, and iron, making them more accessible for absorption in the digestive tract. Additionally, citric acid can help maintain an optimal pH level in the stomach, further aiding in the digestion and absorption of nutrients. It can help increase the bioavailability of magnesium and calcium, which are crucial for bone health and various physiological functions. Lactic Acid Produced during the fermentation process, lactic acid is commonly found in fermented foods such as yogurt and sauerkraut. This organic acid not only contributes to the tangy flavor of these foods but also promotes the growth of beneficial gut bacteria. A healthy gut microbiome is super important for making sure that nutrients, especially minerals, are absorbed properly. Lactic acid can also help lower the pH in the gut, creating an environment that enhances the solubility and absorption of minerals.
Citric acid:
.jpeg)
Citric acid, a prominent organic acid in micronutrition, plays a crucial role in maintaining cellular health and metabolic efficiency. As a key component of the citric acid cycle, also known as the Krebs cycle or TCA cycle, citric acid is integral to the process by which cells generate energy. By participating in this cycle, citric acid helps to produce the ATP necessary for numerous cellular functions, including muscle contraction, nerve impulse transmission, and the synthesis of macromolecules.
The presence of citric acid in the digestive system leads to its interaction with calcium and magnesium, resulting in the formation of soluble complexes. This chemical interaction increases the solubility of these minerals, which facilitates their absorption in the intestines. As a result, the body can more effectively take in these essential nutrients, which is particularly beneficial for individuals who may struggle with mineral deficiencies. Citric acid’s importance extends beyond energy production; it also enhances the absorption of vital minerals. It plays a key role in enhancing the absorption of calcium and magnesium in the body. It does this by forming soluble complexes with these minerals, which facilitates their absorption in the intestines. This effect is particularly significant for individuals with dietary deficiencies or those who rely on plant-based diets, where mineral absorption can be less efficient.
By enhancing mineral absorption, citric acid contributes to bone health, muscle function, and overall metabolic balance. This is especially relevant for those following plant-based diets, where the bioavailability of certain minerals can be lower due to the presence of phytates and oxalates in many plant foods. These substances have the ability to attach to minerals and impede their absorption. By improving the ability to dissolve of calcium and magnesium, citric acid helps to counteract these effects, ensuring that individuals on such diets can still meet their nutritional needs. The implications of improved mineral absorption are far-reaching. Calcium is crucial for maintaining strong bones and teeth, while magnesium plays a vital role in muscle function, nerve transmission, and energy production. Adequate levels of these minerals are essential for preventing conditions such as osteoporosis, muscle cramps, and metabolic disorders.
Role and Function of Citric Acid in Organic Food Sources

Flavor Enhancement
Citric acid, a weak organic acid found naturally in citrus fruits, plays a crucial role in flavor enhancement across a wide range of food and beverage products. Its primary contribution to flavor enhancement is its ability to provide a sharp, tangy taste that can elevate the overall sensory experience of a product. When added to food and beverages, citric acid acts as a flavor acidulant, adjusting the pH levels to enhance the perception of tartness and balance the sweetness. This acidification not only sharpens the taste profile but also increases the overall freshness of flavors, making them more vibrant and pronounced.
The presence of citric acid can modify the sensory attributes of various products by interacting with other ingredients. For instance, in soft drinks and fruit-flavored candies, citric acid amplifies the fruity notes while suppressing any potential off-flavors or unwanted sweetness, thereby creating a more harmonious flavor profile. Its role in flavor enhancement is particularly significant in confectionery, where it can contribute to a more complex and appealing taste experience by mimicking the natural tartness of fruits.
Citric acid is well-known for its ability to enhance the taste of organic foods. It adds a zesty, sour note that can balance and elevate the overall flavor of various products. This is especially crucial in organic foods, where the use of natural and minimally processed ingredients often necessitates flavor adjustments to attract consumers.
Furthermore, citric acid serves as a preservative by lowering the pH of foods, which helps inhibit microbial growth and extends shelf life. This preservative action not only helps maintain the quality and safety of the product but also ensures that the flavor remains consistent over time. As a result, citric acid is a valuable ingredient in maintaining the desired taste and texture of products throughout their shelf life.
In addition to its functional properties, citric acid is often used in combination with other flavor enhancers and acids, such as malic acid or ascorbic acid, to create a more nuanced and well-rounded flavor profile. This synergy can further intensify the sensory impact of a product, making citric acid a versatile tool in the flavoring arsenal of food and beverage manufacturers. The effectiveness of citric acid in flavor enhancement is well-documented, with numerous studies and practical applications in the food industry highlighting its importance in creating enjoyable and high-quality taste experiences
Exploration that citric acid influences taste perception by interacting with taste receptors on the tongue. The findings suggest that citric acid can amplify fruit flavors in organic beverages while decreasing the need for added sugars, which aligns perfectly with the organic food sector's commitment to reducing synthetic additives.
Preservation and Shelf Life Extension
Citric acid is a natural organic acid that is commonly used in food processing because it helps preserve food and extend its shelf life. Its primary mechanism of action in preservation involves acidification, which alters the pH levels of food products. By lowering the pH, citric acid creates an environment that inhibits the growth of spoilage microorganisms and pathogenic bacteria, thereby extending the shelf life of various foods and beverages. This acidulant is particularly effective in preventing the proliferation of bacteria, yeast, and molds, which are often responsible for spoilage and deterioration of food quality.
The preservation capability of citric acid is closely related to its role in the food matrix. In acidic environments, many microbial pathogens struggle to survive and reproduce, which contributes to the overall safety and longevity of food products. For instance, citric acid is commonly used in canned goods, jams, and jellies to maintain acidity levels that inhibit microbial activity and enzymatic reactions that could lead to spoilage. This app keeps the product's texture, taste, and nutrients intact for a long time.
Citric acid plays a crucial role in organic foods as a natural preservative. By lowering the pH of food products, it creates an acidic environment that prevents the growth of spoilage microorganisms and harmful pathogens. This characteristic is particularly beneficial for organic foods, which typically do not contain synthetic preservatives.
Moreover, citric acid acts as a chelating agent, binding with metal ions that could otherwise catalyze oxidative reactions. By sequestering these metal ions, citric acid helps prevent oxidation processes that can lead to rancidity and off-flavors in fatty foods. This property is particularly beneficial in the preservation of oils, dressings, and processed foods, where oxidative stability is crucial for maintaining product quality.
The effectiveness of citric acid in extending shelf life is well-documented in various food systems Research indicates that citric acid can greatly lower the number of microbes in acidic foods, which improves their safety and helps them stay fresh longer. Additionally, its use in conjunction with other preservation methods, such as refrigeration or high-pressure processing, can provide a synergistic effect, further extending the product's shelf life while preserving its sensory and nutritional attributes.
Citric acid's preservation benefits are not limited to its acidifying and chelating actions. It also aids in keeping the color and taste of foods stable by stopping the breakdown of pigments and flavor substances. This stabilization is crucial in maintaining the aesthetic and sensory qualities of products such as fruit juices, sauces, and confectioneries over time.
Study in Food Control highlights how the acidity of citric acid contributes to prolonging the shelf life of organic fruit juices. The findings show that citric acid effectively inhibits microbial growth and helps maintain the quality of the product over time, making it a vital ingredient for ensuring the safety and durability of organic beverages.
In summary, citric acid's role in preservation and shelf life extension is integral to modern food processing. Its ability to acidify, chelate metal ions, and stabilize food products contributes to its widespread use in enhancing the safety, quality, and longevity of a diverse range of food items
Nutrient Bioavailability

Citric acid is a natural organic acid commonly found in citrus fruits. It is important for improving how our bodies absorb nutrients, which is essential for good nutrition. Its primary contribution to this process is its ability to influence the solubility and absorption of various minerals, particularly those that are essential for health, such as calcium, magnesium, and iron. Citric acid enhances the bioavailability of these nutrients through its chelating properties, which involve binding with metal ions and forming soluble complexes. This chelation process makes minerals more soluble in the digestive system, helping them to be absorbed into the blood.
In the case of calcium, citric acid has been shown to improve its absorption by forming calcium citrate, a soluble compound that is more readily absorbed in the intestines compared to other calcium salts. This effect is particularly beneficial in individuals with low dietary calcium intake or those at risk of osteoporosis, as it helps ensure adequate calcium levels for bone health). Similarly, citric acid enhances the absorption of magnesium by forming soluble magnesium citrate, which aids in the efficient uptake of this essential mineral, crucial for various physiological functions including muscle and nerve activity, along with bone wellness.
Moreover, citric acid also plays a role in improving iron absorption, particularly non-heme iron, which is found in plant-based foods Citric acid helps non-heme iron dissolve better, which makes it easier for the body to take in. This is particularly important for vegetarians and individuals with iron-deficiency anemia, as non-heme iron is less bioavailable compared to heme iron from animal sources . The chelation of iron by citric acid reduces the impact of dietary inhibitors of iron absorption, such as phytates and polyphenols, thereby enhancing overall iron uptake.
In addition to its impact on mineral absorption, citric acid influences the digestion and metabolism of various nutrients. By lowering the pH in the stomach, it can promote the activity of digestive enzymes, facilitating the breakdown and absorption of nutrients from food. This role in digestive health further supports the overall nutritional status and well-being of individuals .
Overall, citric acid’s ability to enhance nutrient bioavailability underscores its importance in nutrition and health. By improving the absorption of key minerals and supporting digestive processes, citric acid contributes to more effective utilization of dietary nutrients, which is essential for maintaining optimal health and preventing nutritional deficiencies .
pH Control and Stability
Citric acid is super important for keeping the pH levels in organic foods just right. By fine-tuning and stabilizing the pH levels, citric acid ensures that various food products retain their intended consistency and texture. Food Chemistry journal explores how citric acid contributes to maintaining stable pH levels in organic sauces and dressings. The research emphasizes that citric acid is key to preserving the desired texture and flavor of these products, making sure they stay appealing and effective throughout their shelf life.
Antioxidant Benefits
.jpg)
Citric acid, an organic acid found abundantly in citrus fruits, provides significant antioxidant properties that play a crucial role in cellular protection and overall well-being. While citric acid itself is not a potent antioxidant, it plays a crucial role in enhancing the effectiveness of other antioxidants and mitigating oxidative stress. In the Krebs cycle, citric acid is converted into several intermediate metabolites that are essential for the generation of reducing agents, such as NADH and FADH2, which are crucial for cellular energy production and maintenance of redox balance. These reducing agents contribute to the body’s overall antioxidant capacity by participating in various biochemical reactions that neutralize free radicals and reactive oxygen species (ROS), thus protecting cells from oxidative damage. This indirect role in the antioxidant defense system helps reduce the risk of oxidative stress-related diseases, including cardiovascular diseases and neurodegenerative disorders.
By chelating metal ions, which can catalyze oxidative reactions, citric acid prevents these metals from promoting the formation of free radicals. This chelating action reduces the oxidative degradation of lipids, proteins, and other sensitive molecules, thereby preserving the quality and nutritional value of food products. In this way, citric acid contributes to the preservation of antioxidant compounds, such as vitamins C and E, which are vital for maintaining cellular health and protecting against oxidative damage.
In addition to its main roles, citric acid possesses antioxidant qualities that enhance the nutritional profile of organic foods. Antioxidants play a crucial role in counteracting free radicals, which can lead to oxidative harm to cells and various health problems. Furthermore, citric acid is highlighted for its ability to maintain the antioxidant levels in organic fruits while they are stored. Studies indicate that citric acid effectively preserves the antioxidant activity of these fruits, boosting their overall health benefits.
Citric acid is a versatile organic acid that plays several important roles in organic foods. It boosts flavor, prolongs shelf life, enhances nutrient absorption, balances pH levels, and offers antioxidant properties. These qualities make citric acid an essential ingredient in organic food formulations, contributing to the overall quality and nutritional benefits of these items.
Overall, citric acid’s antioxidant benefits are multifaceted, encompassing both its supportive role in the Krebs cycle and its ability to enhance the stability and efficacy of other antioxidants. By participating in the reduction of oxidative stress and supporting the integrity of antioxidant defenses, citric acid contributes to the protection of cells and tissues from oxidative damage, underscoring its importance in both nutritional and food preservation contexts
Acetic acid
Acetic acid, a simple yet impactful organic compound, plays a crucial role in both metabolism and nutrition. Acetic acid, the main ingredient in vinegar, is recognized for its characteristic sour flavor and various physiological impacts. In the body, acetic acid is involved in several important functions. A key function of it is in the metabolism of energy. It is a key player in the production of acetyl-CoA, a central molecule that enters the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) within the mitochondria. This cycle is essential for the conversion of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy carrier in cells. By facilitating this process, acetic acid helps support cellular energy production, which is critical for maintaining overall bodily functions.
Furthermore, acetic acid significantly influences glucose metabolism and enhances insulin sensitivity. Research has shown that acetic acid can improve insulin sensitivity, which helps regulate blood sugar levels more effectively. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of insulin resistance, as acetic acid may help in stabilizing blood glucose levels and reducing postprandial spikes.
Acetic acid also contributes to digestive health and nutrient absorption. It promotes the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, which are essential for a healthy digestive system and balanced microbiome. In addition, acetic acid improves the absorption of specific minerals, including calcium, by creating soluble complexes that facilitate easier uptake by the intestines. This can have positive implications for bone health and overall mineral utilization in the body.
Acetic acid, which is a primary ingredient in vinegar, serves various important purposes in organic food products. Its role goes beyond just adding flavor; it also aids in preservation, helps regulate pH levels, and may offer health benefits. This organic acid is commonly found in fermented foods and acts as a natural preservative, playing a crucial part in enhancing the quality and stability of organic foods. Let’s explore the functions and significance of acetic acid in organic food sources, backed by academic studies.
The Role and Importance of Acetic Acid in Organic Food Sources
Preservation and Longevity
Acetic acid, a simple organic acid with a distinct sour taste, plays a pivotal role in the preservation and longevity of various foods. Its effectiveness as a preservative is largely attributed to its ability to acidify food products, thereby creating an environment that is inhospitable to the growth of spoilage microorganisms and pathogens. When acetic acid is used in food preservation, it lowers the pH of the food, which inhibits the activity of bacteria, yeast, and molds that could otherwise lead to spoilage and reduced shelf life.
The preservation of food by acetic acid operates through its role as a bacteriostatic agent, effectively inhibiting bacterial growth. By reducing the pH to levels where many microorganisms cannot thrive, acetic acid effectively extends the shelf life of products such as pickles, sauces, and condiments. This acidification also contributes to the inhibition of enzymatic activities that can lead to deterioration in texture, flavor, and nutritional quality In the process of pickling, the elevated acidity of acetic acid not only provides a distinctive tangy taste but also guarantees that the vegetables are protected from microbial contamination and deterioration.
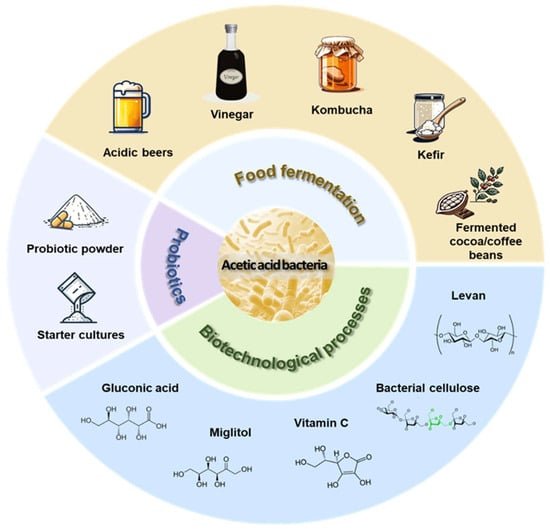
Acetic acid’s role in preservation is further enhanced by its ability to act as a preservative in combination with other ingredients and methods. In many pickled products, the presence of acetic acid not only prevents microbial growth but also synergistically works with salt, spices, and other preservatives to enhance overall product safety and stability. This combined approach allows for the development of a well-rounded preservation system that extends the longevity of the food product while maintaining its sensory and nutritional qualities.
Acetic acid is well-known for its preservative qualities, which play a crucial role in prolonging the shelf life of organic food items. Its effectiveness as a preservative stems from its capacity to reduce the pH of food, creating an acidic environment that hinders the growth of spoilage microorganisms and harmful pathogens. Research has explored the antimicrobial effects of acetic acid in organic pickles and sauces. The findings revealed that acetic acid successfully manages microbial growth, thereby enhancing the longevity of these products. By sustaining a low pH level, the acid inhibits the proliferation of bacteria and molds, thereby ensuring the safety and stability of organic foods.
Moreover, acetic acid's preservation benefits extend beyond its direct antimicrobial effects. It also plays a role in inhibiting oxidation processes that can lead to rancidity and spoilage in fatty foods. By lowering the pH and creating a more acidic environment, acetic acid helps stabilize the fat content in products such as dressings and marinades, thereby prolonging their freshness and quality. This stabilization is crucial in maintaining the flavor and nutritional value of these products over their shelf life.In addition to its role in food preservation, acetic acid is utilized in various industrial applications for extending the shelf life of processed foods and beverages. Its effectiveness in maintaining product quality, coupled with its low cost and availability, makes it a valuable ingredient in both household and commercial food preservation practices . Overall, acetic acid's contributions to food preservation and longevity are integral to maintaining product safety, quality, and shelf life. Through its acidifying effects, it inhibits microbial growth, prevents spoilage, and stabilizes food products, making it a crucial component in modern food processing and preservation.
Flavor Boost
Acetic acid, a key component of vinegar, is renowned for its ability to enhance flavor profiles across a diverse range of culinary applications. Its distinctive sharpness and tangy character provide a unique flavor boost that can significantly transform and elevate the taste of foods and beverages. The primary mechanism by which acetic acid influences flavor is through its acidifying properties, which contribute to a more balanced and vibrant taste experience.
When added to foods, acetic acid functions as an acidulant, lowering the pH and thereby enhancing the perception of sourness. This sourness can serve as a counterpoint to sweetness and richness, creating a more complex and satisfying flavor profile. For instance, in salad dressings and marinades, acetic acid imparts a tangy bite that complements the oil and seasonings, making the overall flavor more dynamic and appealing. This effect is particularly valuable in dishes where a balance between sweet, salty, and sour elements is desired.

Acetic acid also plays a crucial role in flavor enhancement through its interaction with other ingredients. In sauces and condiments, such as ketchup and barbecue sauce, the acidity from acetic acid can heighten the flavor of tomatoes and spices, resulting in a more robust and well-rounded taste. By interacting with various flavor compounds, acetic acid can amplify their intensity and improve their overall integration into the product.
Moreover, the role of acetic acid in fermentation processes adds another layer to its flavor-boosting capabilities. During fermentation, acetic acid is
